Introduction: The Need for Sustainable Food Production in the Face of Climate Change
As climate change continues to threaten global food security, traditional methods of food production are increasingly being scrutinized for their environmental impact. Agriculture, especially livestock farming, is responsible for a significant portion of global greenhouse gas emissions, deforestation, and water usage. With the global population expected to reach nearly 10 billion by 2050, finding sustainable ways to produce food has never been more critical.
In response to these challenges, technology is stepping in to revolutionize the food production process. From lab-grown meat to smart agriculture systems, technological advancements are offering innovative solutions to reduce the environmental footprint of food production while ensuring the world can meet the nutritional demands of a growing population. These innovations are not just reshaping the food industry—they are transforming how we think about sustainability, nutrition, and the future of food.
This article explores the ways in which technology is driving the future of sustainable food production, highlighting the most promising innovations that could revolutionize how we grow, produce, and consume food.
Lab-Grown Meat: A Sustainable Solution to Traditional Livestock Farming
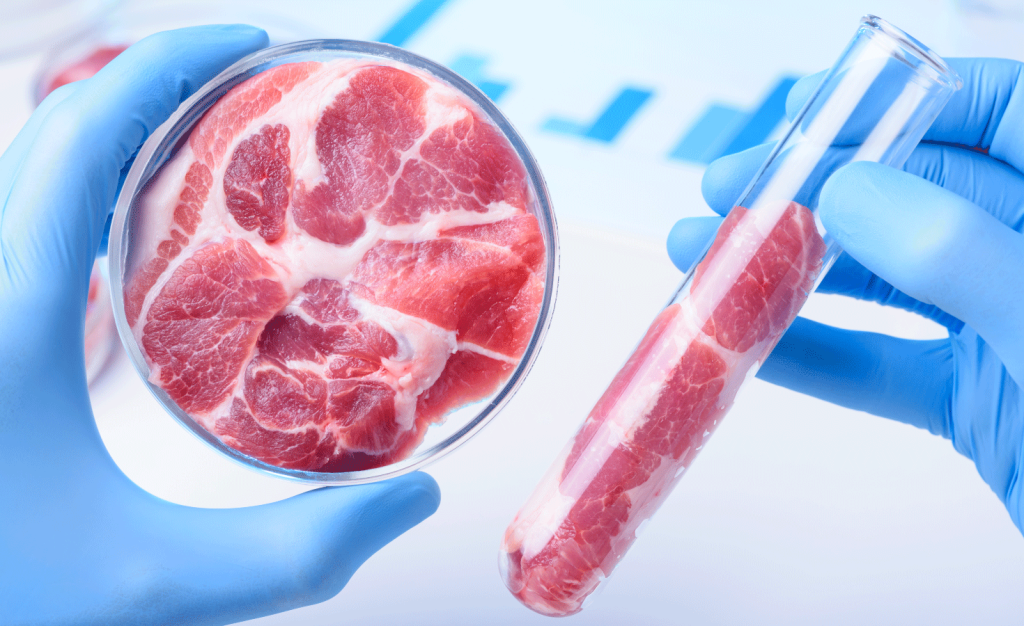
One of the most exciting developments in sustainable food production is lab-grown meat, also known as cultured or cellular meat. Traditional livestock farming has long been associated with environmental problems, including land degradation, excessive water use, and significant carbon emissions. Lab-grown meat, which is produced by cultivating animal cells in a lab rather than raising and slaughtering animals, promises to offer a more sustainable alternative.
Cultured meat is produced by taking a small sample of animal cells and growing them in a controlled environment to form muscle tissue. The result is real meat that closely resembles its traditionally farmed counterpart, but with a fraction of the environmental impact. This technology reduces the need for vast swaths of land, the use of feed crops, and the release of harmful emissions associated with raising livestock. It also eliminates the ethical concerns associated with animal slaughter, providing a more humane way to produce meat.
While lab-grown meat is still in its early stages and faces challenges such as production cost, scalability, and regulatory approval, it holds great promise as a key solution to sustainable food production in the future. As production processes become more efficient and prices decrease, lab-grown meat could become a mainstream option for environmentally conscious consumers.
Vertical Farms: How Urban Farming Technologies Are Reducing Food Miles
Urbanization has led to a dramatic increase in the demand for food that must be transported over long distances, a practice that contributes to high carbon emissions. Vertical farming is a solution that not only reduces food miles but also addresses the challenges of urban space constraints. These innovative farming systems involve growing crops in stacked layers within controlled indoor environments, often located in urban areas.
Vertical farms utilize advanced technologies such as hydroponics and aeroponics (growing plants with minimal soil or water) to optimize space and resource usage. By growing food locally in urban centers, vertical farms can drastically reduce transportation costs and associated carbon emissions, all while providing fresh, nutritious produce year-round.
In addition to reducing food miles, vertical farming also uses less water than traditional farming methods and can be done in environments where conventional agriculture is not feasible. These farms are ideal for urban areas, turning unused spaces such as abandoned buildings, warehouses, and rooftops into productive farming operations. Vertical farming not only helps reduce the environmental footprint of food production but also increases food security by making fresh produce more accessible in cities.
Aquaponics and Hydroponics: Eco-Friendly Farming Systems for Urban Environments
Aquaponics and hydroponics are two innovative farming systems that have gained attention for their ability to produce food in urban environments while minimizing water and land usage. Both methods are examples of how technology can optimize resource use to make food production more sustainable.
- Aquaponics: Aquaponics combines fish farming (aquaculture) with hydroponic plant growing. The waste produced by the fish provides organic nutrients for the plants, while the plants help filter and clean the water for the fish. This creates a self-sustaining, closed-loop system that uses minimal water and energy. Aquaponics can be used to grow a wide range of crops, such as leafy greens, herbs, and even some fruit, while also raising fish for food.
- Hydroponics: Hydroponics involves growing plants without soil by using a nutrient-rich water solution. This method is highly water-efficient, using up to 90% less water than traditional soil-based agriculture. Hydroponic systems are often used in indoor farming settings, such as greenhouses or vertical farms, and can grow a variety of crops, including tomatoes, lettuce, and strawberries. Because hydroponics doesn’t require soil, it can be used in areas with poor or contaminated soil, making it a highly adaptable solution for sustainable food production.
Both aquaponics and hydroponics reduce the environmental impact of traditional farming by cutting down on water usage, eliminating the need for chemical pesticides, and minimizing land use. These systems also enable year-round crop production, ensuring a stable food supply in urban areas.
Smart Agriculture: Using Tech to Optimize Resources and Reduce Waste
Smart agriculture, or precision farming, uses advanced technologies like sensors, drones, and artificial intelligence (AI) to optimize farming practices, reduce waste, and improve resource efficiency. These technologies help farmers monitor crop health, soil conditions, weather patterns, and irrigation needs in real time, enabling them to make data-driven decisions that maximize yields while minimizing environmental impact.
- Sensors and IoT Devices: Soil sensors, moisture detectors, and temperature sensors allow farmers to monitor growing conditions more precisely. This technology helps farmers apply water, fertilizer, and pesticides only when and where they are needed, reducing waste and minimizing chemical use.
- Drones and Aerial Imaging: Drones equipped with high-resolution cameras and multispectral sensors can survey large agricultural fields, identifying areas of stress or disease before they become visible to the naked eye. This allows for targeted interventions, reducing the need for broad pesticide application and minimizing environmental harm.
- AI and Machine Learning: AI algorithms analyze data from sensors, drones, and weather forecasts to predict the optimal time for planting, harvesting, and applying resources. Machine learning can also help farmers identify patterns and predict outcomes, making farming operations more efficient and profitable.
Smart agriculture helps reduce resource consumption by enabling farmers to work more efficiently, thereby lowering greenhouse gas emissions, water usage, and fertilizer waste. By improving the sustainability of traditional farming methods, smart agriculture is paving the way for a more eco-friendly future in food production.
Plant-Based Innovations: The Rise of Sustainable Plant-Based Food Tech
Plant-based food technology has seen an explosion in innovation in recent years, driven by increasing consumer demand for sustainable alternatives to animal-based products. From plant-based meat to dairy-free milk and egg substitutes, food technology is transforming how we produce and consume plant-based foods.
- Plant-Based Meat Alternatives: Companies like Beyond Meat and Impossible Foods are creating plant-based meat alternatives that closely mimic the taste, texture, and appearance of traditional meat products. These innovations use ingredients such as pea protein, soy, and mushrooms to create meat substitutes that are both environmentally friendly and nutritionally similar to their animal-based counterparts. Plant-based meats have a significantly lower carbon footprint compared to beef or pork production, as they require less land, water, and energy to produce.
- Dairy-Free Innovations: With growing concerns about the environmental impact of dairy farming, plant-based dairy alternatives like almond milk, oat milk, and coconut yogurt are becoming increasingly popular. These alternatives require fewer resources to produce and are also free from the ethical concerns associated with animal-based dairy products.
- Innovative Plant-Based Packaging: In addition to food products, the rise of plant-based materials is transforming packaging technology. Companies are developing edible packaging and compostable containers made from plant-based ingredients, which can further reduce plastic waste and environmental harm.
The shift toward plant-based innovations in food technology not only offers sustainable alternatives to traditional animal-based products but also supports efforts to reduce the environmental impact of food production at large. As these innovations continue to evolve, plant-based food technologies will play an increasingly central role in building a more sustainable food system.
Conclusion: How Technological Advancements in Food Production Are Transforming Sustainability
Technological advancements in food production are revolutionizing how we think about sustainability, from lab-grown meat to vertical farms and plant-based innovations. These technologies offer viable solutions to the challenges of feeding a growing global population while reducing the environmental impact of food production. By optimizing resources, minimizing waste, and utilizing renewable energy sources, these innovations are reshaping the future of food.
In 2025 and beyond, the convergence of cutting-edge technology with sustainable farming practices will continue to drive change across the food industry. The future of food production is not just about feeding people—it’s about doing so in a way that preserves the health of the planet and promotes a more sustainable, resilient food system for generations to come.
As consumers, we have the opportunity to support these innovations by choosing sustainable food options and embracing the technologies that are shaping the future of nutrition. With continued investment in green food tech, we can pave the way for a healthier, more sustainable planet.










































Discussion about this post