In today’s hyper-connected world, data is more valuable than ever. Every day, trillions of bytes of personal, corporate, and government data are generated, processed, and stored across the globe. The rise of cloud computing, IoT (Internet of Things), and artificial intelligence has only intensified the importance of safeguarding this data. But as the volume of data grows, so do the threats to its security. From data breaches to ransomware attacks, the question isn’t just about how much data we have—it’s about how much we can protect.
If your data isn’t safe, what is?
1. The Importance of Data Security
In a world that operates on data, its security is not just an IT concern—it is a fundamental issue for personal privacy, business integrity, and national security. Data breaches are not only costly but can also result in the loss of trust, brand reputation, and regulatory penalties. According to a report by IBM, the average cost of a data breach in 2023 was around $4.45 million, a staggering figure for any organization.
But why does data matter so much? Data holds the key to who we are—our identities, habits, preferences, financial records, and communications. When data is compromised, it goes beyond just numbers and facts; it becomes a direct threat to the individual or organization it belongs to.
2. The Landscape of Modern Cybersecurity Threats
2.1 Data Breaches: The Silent Crisis
Data breaches have become a common phenomenon in the digital age. These breaches can occur due to hacking, system vulnerabilities, insider threats, or poor data handling practices. Recent high-profile data breaches, like the ones suffered by Equifax and Target, highlight just how vulnerable large organizations can be. Once an attacker gains access to sensitive data, they can use it for identity theft, financial fraud, or sell it on the dark web.
2.2 Ransomware: The Digital Extortion
Ransomware attacks have skyrocketed in the past few years. In these attacks, malicious software encrypts the victim’s data, rendering it inaccessible until a ransom is paid. Ransomware attackers are often highly organized groups, demanding significant sums of money in cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin. The consequences of a successful ransomware attack can be catastrophic, especially for industries like healthcare or finance, where data availability is critical.
2.3 Phishing: The Art of Deception
Phishing attacks are another popular method used by cybercriminals. In a phishing attack, the attacker disguises themselves as a trusted entity to lure victims into revealing sensitive information such as usernames, passwords, or credit card numbers. Phishing scams are becoming increasingly sophisticated, with attackers using social engineering tactics to trick even the most experienced users.

3. Why Traditional Security Measures Aren’t Enough
For years, traditional security measures like firewalls, antivirus software, and encryption have been the go-to solutions for data protection. While these tools have certainly helped defend against cyberattacks, they are no longer enough in today’s threat landscape. The growing sophistication of cybercriminals and the increasing number of attack vectors—especially with the rise of cloud computing—means that organizations need to rethink their approach to data security.
3.1 The Cloud Paradox
While cloud computing offers unprecedented flexibility, scalability, and cost savings, it also creates new risks. Many organizations move their data to the cloud without fully understanding the security implications. Cloud services can be vulnerable to data breaches, and misconfigurations by users can expose sensitive data to cybercriminals.
A major challenge is the shared responsibility model in cloud security. While cloud service providers (CSPs) are responsible for securing the infrastructure, customers must ensure the security of their data and applications running on the cloud. Misunderstanding this division of responsibilities has led to a number of high-profile cloud security failures.
3.2 The Human Element
One of the most overlooked aspects of data security is the human element. Employees often act as the first line of defense, but they are also the weakest link. Human error, lack of awareness, and insider threats can all result in data breaches. According to a report by the Ponemon Institute, 60% of data breaches are caused by employee negligence. This underscores the importance of training and developing a security-conscious culture within organizations.
4. Advanced Strategies for Data Protection
As data security threats evolve, so must the strategies used to protect it. Modern cybersecurity requires a multi-layered approach that combines technology, processes, and human factors. Below are some advanced strategies that organizations can adopt to safeguard their data:
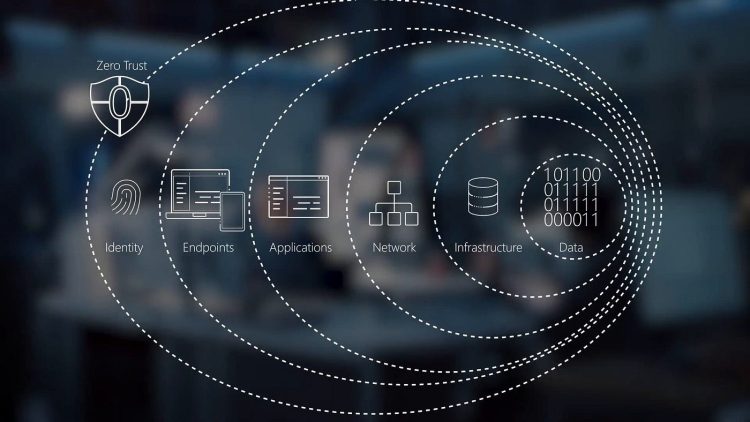
4.1 Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA)
The concept of Zero Trust is gaining momentum in the cybersecurity world. The basic principle of Zero Trust is that no one—inside or outside the organization—is trusted by default. Every user, device, and application must be authenticated and continuously verified before gaining access to data or systems. This approach reduces the attack surface and makes it harder for attackers to gain unauthorized access.
4.2 End-to-End Encryption
Encryption is a critical tool for protecting data both in transit and at rest. However, end-to-end encryption takes this a step further by ensuring that only the intended recipients can decrypt and access the data. This ensures that even if data is intercepted or accessed by unauthorized parties, it remains unreadable and useless to them.
4.3 Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
MFA is a powerful security mechanism that requires users to provide multiple forms of identification before accessing systems or data. Even if an attacker manages to steal a user’s password, MFA adds another layer of security, making it much harder for them to gain access. Common MFA methods include fingerprint scanning, facial recognition, and one-time passcodes sent via SMS or email.
4.4 Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) for Threat Detection
AI and machine learning technologies are revolutionizing the way we detect and respond to security threats. By analyzing large volumes of data in real-time, AI systems can identify abnormal patterns or behaviors that might indicate a cyberattack. This allows organizations to respond faster and more effectively to emerging threats, reducing the time between attack and mitigation.

5. The Future of Data Security
As the digital landscape continues to evolve, so will the tactics and tools used by cybercriminals. The future of data security will likely see greater integration of automation, artificial intelligence, and blockchain technology to provide stronger, more resilient protection for sensitive information.
Blockchain, for instance, is being explored as a potential solution for securing data due to its decentralized and immutable nature. By ensuring that data cannot be altered or deleted without consensus from all parties involved, blockchain could provide a new level of trust and security in data storage and transmission.
Additionally, the rise of quantum computing presents both a challenge and an opportunity for data security. While quantum computers could potentially break current encryption algorithms, they also offer the possibility of developing new, quantum-resistant encryption methods that would be virtually unbreakable by conventional means.
6. Protecting Your Personal Data
For individuals, the threats to personal data are equally real. From social media accounts to online shopping platforms, our personal information is constantly at risk. So, how can you protect yourself in this digital age?
6.1 Strong Passwords and Password Managers
Creating strong, unique passwords for every online account is one of the simplest yet most effective ways to safeguard personal data. Password managers can help you generate and store complex passwords securely, so you don’t have to remember them all.
6.2 Be Cautious with Public Wi-Fi
Public Wi-Fi networks, such as those in coffee shops or airports, are prime targets for cybercriminals. Avoid accessing sensitive information like banking apps or email accounts while on these networks. If you must use public Wi-Fi, consider using a Virtual Private Network (VPN) to encrypt your internet connection and protect your data.
6.3 Regular Software Updates
Software vendors regularly release updates to fix vulnerabilities and patch security flaws. Make sure to install these updates as soon as they are available. Many cyberattacks exploit known vulnerabilities in outdated software, making regular updates crucial to staying safe.
7. Conclusion: The Ever-Evolving Battle for Data Security
In conclusion, the importance of data security cannot be overstated. As we move into an increasingly interconnected world, protecting data has become one of the greatest challenges of our time. While traditional security measures still play a role, organizations and individuals must adopt more advanced and comprehensive approaches to protect sensitive data from emerging threats.
The question is no longer just “How can we secure our data?” but “How can we stay ahead of the evolving threats?” The future of data security will rely on a combination of cutting-edge technologies, human awareness, and a culture of proactive defense.
If your data isn’t safe, what is?










































Discussion about this post