Renewable energy is at the heart of the world’s efforts to fight climate change, reduce dependence on fossil fuels, and secure a sustainable future. As technology continues to evolve and environmental concerns intensify, the next big breakthrough in renewable energy could be a game-changer—ushering in a new era of efficiency, affordability, and accessibility. So, what will this breakthrough look like? What are the trends and innovations poised to redefine the way we generate, store, and consume energy?
In this article, we will explore the promising technologies and trends that could take renewable energy to the next level. From solar power innovations to breakthroughs in energy storage, here’s a glimpse into what the future holds for clean, sustainable energy.
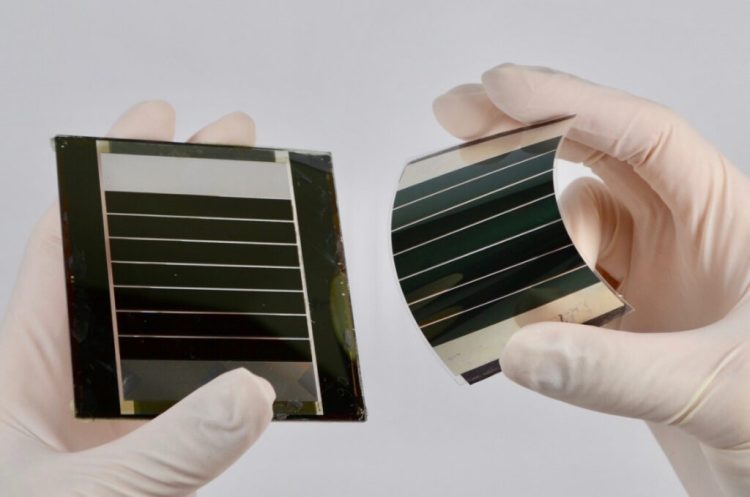
1. The Rise of Perovskite Solar Cells
Solar energy has made remarkable strides over the past decade, with traditional silicon-based solar panels becoming more efficient and affordable. However, the next leap in solar technology might come from a surprising source: perovskite solar cells.
Perovskites are a class of materials that have shown incredible potential in solar power generation. These materials, which have a unique crystal structure, are not only cheaper to produce than traditional silicon-based cells, but they can also be manufactured using simpler methods like inkjet printing. This makes perovskite solar cells a promising candidate for large-scale, low-cost solar power production.
Perovskite solar cells have already achieved impressive efficiencies—some reaching over 25%—and researchers are making breakthroughs in improving their stability and scalability. With ongoing advancements, we may soon see perovskite-based solar panels becoming a mainstream option for homes and industries, drastically reducing the cost of solar energy while improving its performance.
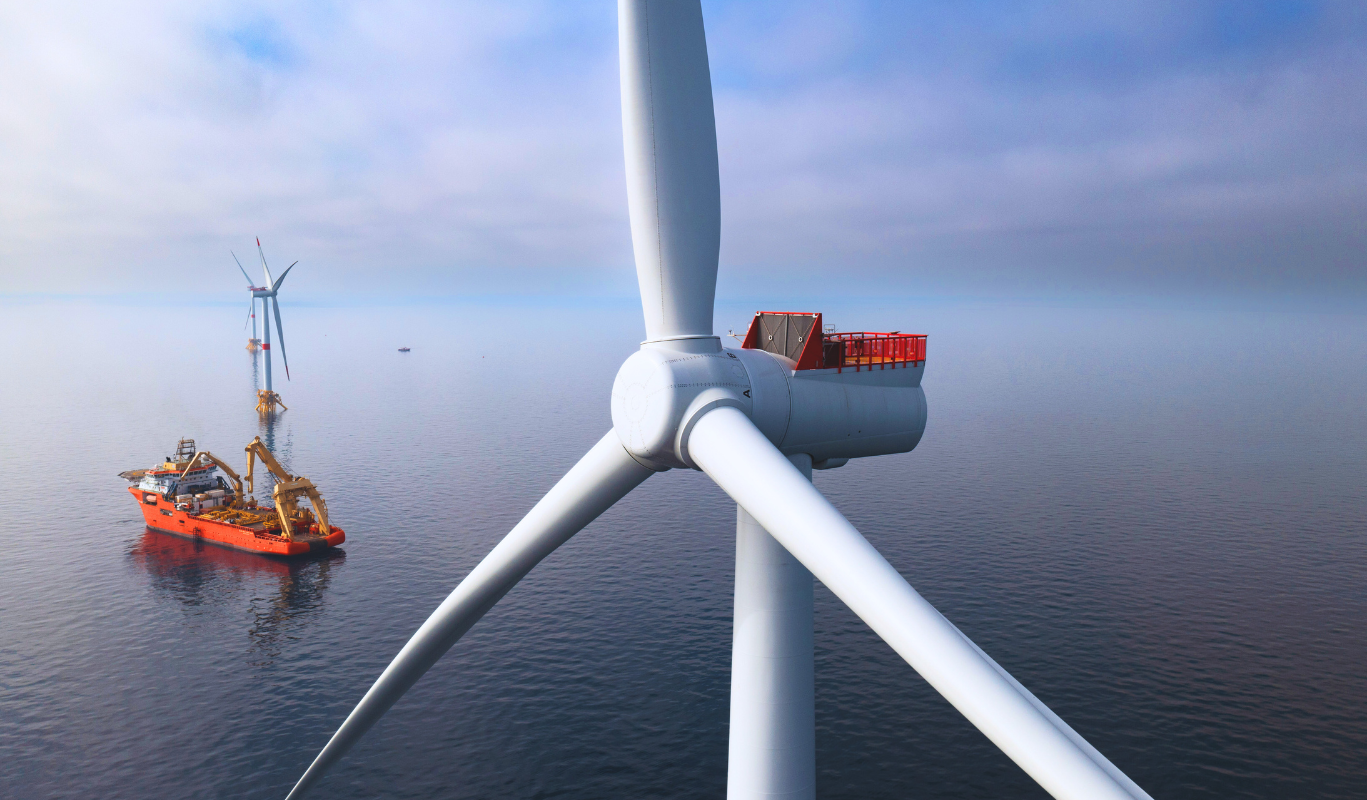
2. Floating Wind Farms: Harnessing the Power of the Sea
Offshore wind farms have long been recognized as a potent source of renewable energy, especially in regions with strong coastal winds. However, traditional offshore wind farms require fixed structures anchored to the seabed, which can limit their deployment in deeper waters.
Enter floating wind farms—a groundbreaking development that allows turbines to be placed in deeper waters, where wind speeds are often higher and more consistent. These floating turbines are anchored to the ocean floor using buoyant platforms, and they can be deployed far offshore, where they’re less likely to interfere with shipping lanes or marine life.
Floating wind farms have the potential to unlock a vast new area for wind energy generation. The technology is already being tested and deployed in several parts of the world, with projects underway in Europe, the US, and Asia. As the technology matures, it could provide a significant portion of global energy needs, contributing to the decarbonization of the power sector.
3. Advanced Energy Storage: The Holy Grail of Renewable Power
One of the biggest challenges with renewable energy, especially solar and wind, is that it doesn’t always align with demand. The sun doesn’t always shine, and the wind doesn’t always blow. This intermittency creates a need for reliable energy storage solutions that can store excess energy when production is high and release it when production is low.
While battery technology has improved in recent years, we still don’t have the perfect storage solution for large-scale renewable energy. But the next breakthrough in energy storage could change everything. Several innovative technologies are on the horizon that could dramatically improve the way we store energy.
- Solid-State Batteries: These batteries replace the liquid electrolytes used in conventional lithium-ion batteries with a solid material. This could lead to batteries that are not only more energy-dense but also safer and longer-lasting.
- Flow Batteries: Flow batteries store energy in liquid form and can be scaled up more easily than solid-state batteries. They could be used to store large amounts of energy for grid-level applications, making them ideal for renewable energy storage.
- Green Hydrogen: Hydrogen, produced using renewable energy (green hydrogen), could be stored and used as a clean fuel. Hydrogen fuel cells are already being used in some transportation sectors, but large-scale storage could make hydrogen a key player in balancing renewable energy grids.
These breakthroughs could help to eliminate the intermittency problem that currently limits renewable energy’s potential, allowing for cleaner, more reliable power systems that don’t rely on fossil fuels.

4. The Role of Artificial Intelligence in Renewable Energy Management
Artificial intelligence (AI) is transforming many industries, and renewable energy is no exception. AI has the potential to revolutionize how we manage and optimize energy production, distribution, and consumption.
AI algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data from weather forecasts, energy demand, and real-time grid conditions to predict the optimal times to generate and store renewable energy. For example, AI can forecast when solar or wind energy production will peak and automatically adjust storage or distribution to ensure energy is available when needed.
Furthermore, AI can help in grid management by enabling smarter, more efficient grids. Smart grids powered by AI can dynamically adjust to fluctuations in energy supply and demand, reducing waste and ensuring energy is delivered where it’s most needed. In the future, AI could even enable decentralized energy networks, where households and businesses generate, store, and trade energy autonomously.
5. Solar Paints and Transparent Solar Panels: The Next Generation of Solar Power
While traditional solar panels require large, dedicated spaces, the future of solar energy could involve integrating solar technology directly into the fabric of our homes, buildings, and even clothing. Solar paints and transparent solar panels are emerging technologies that could make this possible.
- Solar Paint: Scientists are working on creating a paint that can capture sunlight and convert it into electricity. These paints would contain photovoltaic materials that could be applied to the surfaces of buildings, vehicles, and even smartphones. If successful, solar paint could revolutionize the way we think about solar energy by transforming almost any surface into a potential energy generator.
- Transparent Solar Panels: These panels can be integrated into windows and glass facades, allowing buildings to generate their own energy while maintaining transparency. Transparent solar panels could be used in office buildings, residential homes, and even automobiles, helping to reduce the reliance on external energy sources.

These technologies promise to expand the reach of solar energy beyond traditional rooftops, making it possible for almost any surface to generate renewable power.
6. Tidal and Wave Energy: The Untapped Power of the Ocean
We’ve seen incredible progress with wind and solar energy, but one area that remains largely untapped is ocean energy—specifically tidal and wave power. Both tidal and wave energy harness the power of the ocean’s movement to generate electricity.
Tidal power works by capturing the energy from the rise and fall of ocean tides, while wave energy converts the movement of the water’s surface into electricity. Unlike solar or wind power, ocean energy is highly predictable and consistent, making it a promising alternative source of renewable energy.
Several experimental tidal and wave energy projects are already underway, but scaling this technology to a global level has proven challenging. However, as ocean energy technology improves, it could provide a reliable and environmentally friendly power source for coastal regions around the world.
7. The Promise of Bioenergy with Carbon Capture and Storage (BECCS)
Bioenergy with carbon capture and storage (BECCS) represents an innovative approach to addressing both energy production and climate change. BECCS involves producing energy from organic materials (like biomass) while capturing the carbon dioxide emitted during the process and storing it underground.
This “carbon-negative” technology could potentially remove more CO2 from the atmosphere than it emits, helping to reduce global carbon levels while generating energy. BECCS is still in the experimental phase, but it has the potential to be a powerful tool in the fight against climate change, particularly in hard-to-decarbonize sectors like heavy industry and aviation.
8. Microgrids and Distributed Energy Systems: Decentralizing Power Generation
In many parts of the world, particularly in developing countries, access to reliable electricity is a major issue. However, with the rise of microgrids and distributed energy systems, this could change dramatically. Microgrids are localized energy networks that can operate independently from the main grid, using a mix of renewable energy sources like solar, wind, and biomass.
These systems allow communities to generate and store their own power, improving resilience to grid failures and reducing reliance on fossil fuels. Microgrids are already being deployed in remote areas, disaster-prone regions, and even urban settings where they can complement the existing grid infrastructure.
Distributed energy systems, which involve smaller, decentralized power generation units, are also gaining traction. Solar panels on homes, small wind turbines, and community-level energy storage systems can all contribute to a more flexible, decentralized energy infrastructure. These systems could empower individuals and communities to take control of their energy production and consumption.
Conclusion: The Future of Renewable Energy
The next big breakthrough in renewable energy will likely involve a combination of technological advancements in various sectors, including solar, wind, energy storage, and grid management. Whether it’s the rise of perovskite solar cells, the development of floating wind farms, or the application of AI to optimize energy systems, the future of renewable energy is filled with promise.
These breakthroughs will not only make renewable energy more efficient and accessible but also help pave the way for a cleaner, more sustainable world. With continued research, investment, and collaboration, the next big leap in renewable energy could be just around the corner.










































Discussion about this post