Climate change is arguably the most pressing issue of our time, and as the planet grapples with rising temperatures, extreme weather events, and shifting ecosystems, the search for solutions intensifies. From renewable energy innovations to carbon capture technologies, we’ve seen a broad spectrum of responses. But one area that has garnered both attention and skepticism is artificial intelligence (AI). Could AI be the key to mitigating climate change, or does it exacerbate the crisis by adding to energy consumption and contributing to environmental degradation? In this article, we’ll explore both sides of the debate, examining how AI could potentially help or harm efforts to combat climate change.
AI as a Tool for Climate Solutions
Artificial intelligence has already shown promise in a variety of industries, and climate change is no exception. Here are several ways AI can help fight climate change:
1. Optimizing Energy Consumption
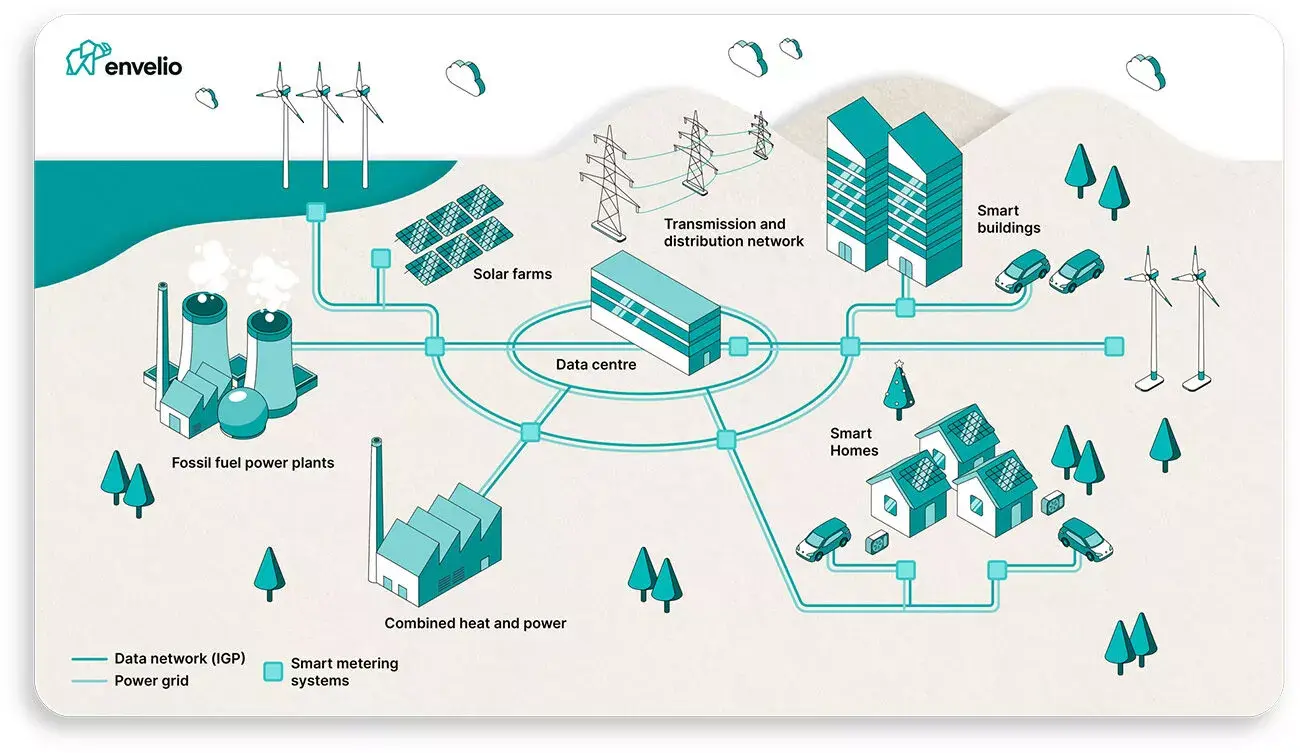
AI can revolutionize how we produce and consume energy. Smart grids powered by AI can optimize the distribution of electricity, minimizing waste and ensuring that energy is used efficiently. By analyzing real-time data, AI can predict when energy demand will peak and adjust power generation accordingly. For instance, AI systems can integrate renewable sources like solar and wind more effectively by predicting fluctuations in supply and matching them with demand patterns.
In homes and businesses, AI-driven systems can automatically adjust heating, cooling, and lighting to optimize energy use, reducing consumption and lowering carbon footprints. For example, smart thermostats like Google Nest use machine learning to understand occupancy patterns and temperature preferences, minimizing the energy needed to heat or cool a space.
2. Renewable Energy Advancement

The transition to renewable energy is one of the most crucial steps in tackling climate change. AI is playing a pivotal role in accelerating this shift. For example, AI algorithms are being used to enhance the efficiency of solar panels by predicting sunlight intensity and optimizing the angle at which the panels are positioned. Similarly, AI is helping to improve wind turbine efficiency by predicting wind patterns and adjusting turbine speeds accordingly.
AI is also being utilized to model energy grids and simulate the integration of renewable energy sources at scale, making it easier to predict and manage the challenges of transitioning from fossil fuels.
3. Climate Modeling and Prediction
Understanding the future impacts of climate change is critical for developing adaptive strategies. AI can analyze vast amounts of climate data to improve weather forecasting models, track long-term climate trends, and predict the impact of various mitigation strategies.
For instance, AI can analyze satellite data to monitor deforestation, track glacial melt, and even predict extreme weather events like hurricanes and droughts. By combining data from different sources, AI can create more accurate models of climate systems, helping policymakers make better decisions regarding mitigation and adaptation efforts.
4. Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS)
Carbon capture and storage technologies are critical to limiting atmospheric CO2 levels. AI is playing a significant role in optimizing these technologies, improving their efficiency and reducing costs. AI systems can analyze geological data to identify the most suitable sites for carbon storage, while also monitoring storage sites to ensure that CO2 remains safely sequestered.
Moreover, AI is being used to design advanced carbon capture systems that can capture CO2 more effectively and at a lower cost, potentially making this solution more scalable and impactful.
5. Sustainable Agriculture
Agriculture is a major contributor to greenhouse gas emissions, but AI can help mitigate its environmental impact. AI-powered precision agriculture tools use data from sensors, drones, and satellites to monitor crop health, soil conditions, and weather patterns. This allows farmers to optimize irrigation, fertilization, and pest control, minimizing resource waste and reducing emissions associated with overuse of water, fertilizers, and pesticides.
By predicting crop yields and climate impacts, AI can also help farmers adapt to changing conditions, ensuring food security while minimizing environmental harm.
AI’s Potential Negative Impact on Climate Change
Despite the numerous potential benefits, AI’s role in climate change is not without its challenges and risks. Some critics argue that AI may exacerbate the problem in several ways:
1. Energy Consumption of AI Systems
AI is a computationally intensive technology that requires vast amounts of energy, especially for training large machine learning models. Training deep learning models, for example, can consume a significant amount of electricity, and much of the data centers that power AI systems rely on non-renewable energy sources.
The rise of AI-driven technologies such as autonomous vehicles, large language models, and real-time data analytics could contribute to higher energy demands, counteracting efforts to reduce emissions. For example, the energy consumption required for training AI models has been shown to increase rapidly as the models become more complex.
2. E-Waste and Resource Extraction
The growing demand for AI technologies also leads to an increase in the production and disposal of electronic devices, contributing to e-waste. The mining of raw materials such as rare earth metals, which are essential for AI hardware, is resource-intensive and often involves environmentally damaging practices.
In some cases, the carbon footprint associated with the production and disposal of AI hardware can outweigh the benefits it provides. For instance, the extraction of lithium for batteries, used in everything from smartphones to electric vehicles, contributes to environmental degradation and pollution.
3. Unequal Access to AI Benefits
AI solutions are often developed and deployed by large tech companies, and their benefits are not always evenly distributed. Wealthy nations or corporations may have the resources to implement AI-driven climate solutions, while poorer regions may be left behind. This disparity could exacerbate existing inequalities, particularly in the context of climate change, where vulnerable communities are already disproportionately affected.
Furthermore, AI solutions may not always be tailored to local needs. A one-size-fits-all approach may not work in regions with different climates, ecosystems, or energy needs, potentially limiting the impact of AI in addressing global climate challenges.
4. Unintended Consequences
As with any new technology, the deployment of AI systems carries the risk of unintended consequences. For example, AI models designed to optimize resource use may inadvertently create new problems. A system that optimizes transportation routes might encourage longer commutes or the construction of new infrastructure, thereby increasing emissions in the long run.
In agriculture, AI-driven systems that focus on optimizing crop yields could lead to overuse of water or fertilizers if they don’t account for environmental constraints, potentially exacerbating environmental degradation.
Striking a Balance: Can AI Truly Help the Fight Against Climate Change?
The relationship between AI and climate change is complex and multifaceted. While AI has enormous potential to help mitigate the impacts of climate change—through energy optimization, renewable energy development, climate prediction, and carbon capture—its own environmental footprint must be carefully managed. The key to unlocking AI’s full potential lies in striking a balance: harnessing AI’s capabilities for the greater good while minimizing its ecological costs.
This will require continued research into energy-efficient AI technologies, as well as policies that promote sustainability in AI development. For example, using renewable energy sources to power AI data centers, improving the recyclability of electronic components, and ensuring that AI solutions are accessible to those most in need will be crucial steps in ensuring that AI becomes a true ally in the fight against climate change.
AI is not a panacea, but when deployed thoughtfully and responsibly, it can certainly play a vital role in helping us address one of the most urgent challenges humanity has ever faced.
Conclusion
The potential for AI to help combat climate change is immense, but so too are the challenges it presents. Whether AI will be a solution or a hindrance to addressing global warming depends largely on how we choose to use it. If we embrace it responsibly, with careful consideration of its environmental impact and equitable distribution, AI can be a powerful tool in the ongoing battle against climate change. However, like all powerful technologies, it requires vigilant oversight, innovation, and a commitment to sustainability to ensure it truly serves the greater good.











































Discussion about this post